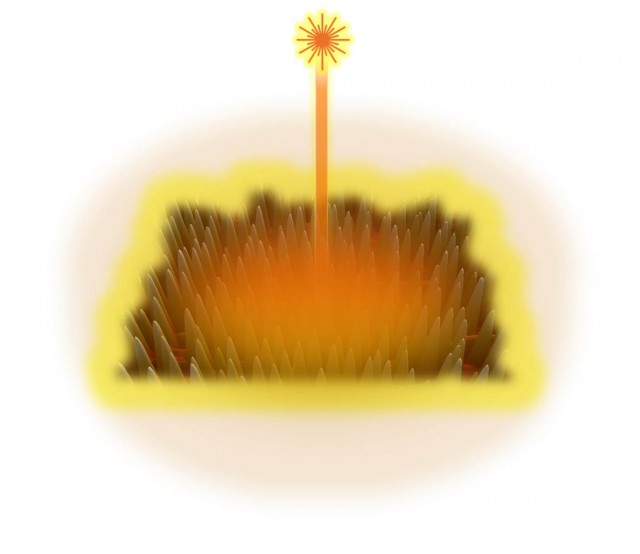
Quantum Dot Laser
Description
This is a touched up AFM rendering of semiconductor InAs quantum dots grown on GaAs by Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE). With each dot spanning only a few nanometers in any direction, tens of billions of them can comfortably fit in an area the size of a penny. Due to their small size, they are quantum mechanical in nature and possess discrete quantum confined energy levels - a real life representation of the 'finite potential well' problem from introductory quantum mechanics courses. In the presence of external stimuli such as photo-excitation or electrical carrier injection, each dot is able to emit photons with wavelengths corresponding to their intrinsic quantum confined energy levels. When placed in a resonant cavity with sufficient external stimuli, the dots become in sync with each-other and emit a coherent laser beam composed of the billions of photons from each individual dot, truly becoming greater than the sum of their parts through this collective lasing action.